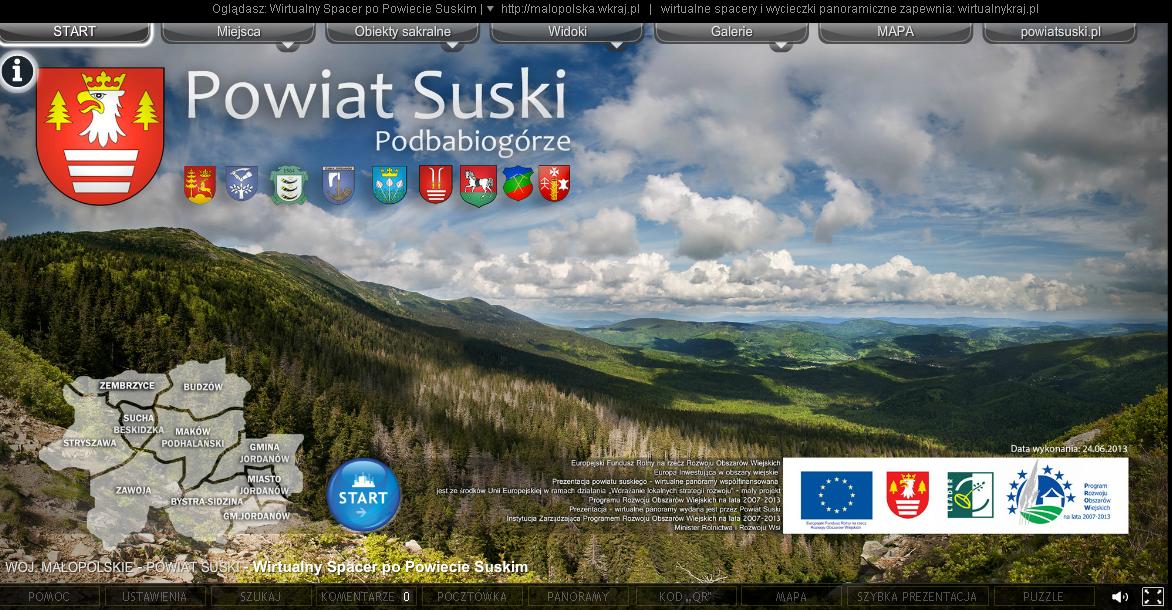
The Suski Poviat is located in the Beskidy Mountains, at the south-western end of the Małopolskie Province, and borders with the Żywiecki Poviat of the Śląskie Province on the west and three other poviats of the Małopolskie Province in the north and east: Wadowicki, Myślenicki and Nowotarski, as well as the local administration unit of Namestovo in Slovakia.
It is a typically mountainous region with forests, taking up almost 50% of its area, being the local natural resource.

The Suski Poviat has 9 communes made by: two towns (Sucha Beskidzka and Jordanów), one rural and urban commune (Maków Podhalański) and six rural communes (Budzów, Bystra-Sidzina, Jordanów, Stryszawa, Zawoja and Zembrzyce). In total, there are 37 towns and villages in the poviat.
The southern part of the poviat, which has the highest altitude, makes the Beskid Żywicki mountain range, which can be divided into three smaller geographical units:
The range of Babia Góra with the highest peak of the entire Beskidy Mountains, Babia Góra (1725 m),

the mountain range of Polica (Polica, 1369 m) and of Jałowiec, also known as the Przedbabiogórskie mountain range (Jałowiec, 1111 m). The characteristic landscape elements of the northern part of the poviat are lower mountain ranges, those of Leskowiec (918 m) and Łamana Skała (929 m) in the Beskid Mały Mountains (in the north-west) and the range of Koskowa Góra (866 m) in the Beskid Makowski Mountains (in the north-east).
Almost the entire area of the poviat lies in the river basin of the upper Skawa, the major river of the region. The three towns located along the Skawa are: Sucha Beskidzka, Maków Podhalański and Jordanów. The most important tributaries of the Skawa in this area are the rivers of Pożoga, Toporzyski Potok, Bystrzanka, Cadynka, Skawica, Grzechynia, Stryszawka and Tarnawka (left-bank), as well as Malejów, Osielec, Wieprzec, Żarnowianka and Paleczka (right-bank). The watershed between the basin of the Baltic Sea and that of the Black Sea is located in the vicinity of the Babia Góra Mount.
The river basin of the Upper Skawa has varied landscape. In the Babia Góra Mountain Range the climate is harsher, the stony soil dominant in the mountains turns into clayey and stony soil in stream valleys. Because of the landscape features, significant parts of this area are difficult to access even today. In the mountain ranges of Beskid Mały and Beskid Makowski the climate is milder and flat mountain river valley bottoms are rich in more fertile brown soil. Lower altitude and less steep slopes have always made these mountains conducive to human migration and settlement.
Natural and cultural values of the poviat as well as its landscape make it an attractive destination for tourists and holiday makers. There is a well-developed network of tourist trails and increasingly more numerous bike routes as well as constantly growing accommodation possibilities.
In order to protect the unique landscape and natural value of the Babia Góra Mount, the Babiogórski National Park was established in the southern part of the poviat in 1954. Many rare and valuable animal species have their habitats in the area of Babia Góra, which includes 166 vertebrate and 2440 invertebrate species.
Endemic Carpathian animal species include: the pine vole – a rodent, and Gaurotes excellens – a beetle. The brown bear, the lynx and the wolf are among the valuable European mammals. The place is also a bird sanctuary and the species found here include the capercaillie and the black grouse – two forest grouses as well as owls: the Ural owl and the eagle owl.
The Babiogórski National Park was included in the international World Network of Biosphere Reserves of the MAB Programme as early as in 1976.
Many animal species listed in the annexes to the Birds Directive and the Habitats Directive live in the Babia Góra area as well as two plant species listed in the Habitats Directive. There are 18 habitats within the area that are considered as valuable on the European scale.
 The list of species under protection includes those listed under the Berne Convention (1979) whose aim is to conserve the wild flora and fauna and their natural habitats which require cooperation between states.
The list of species under protection includes those listed under the Berne Convention (1979) whose aim is to conserve the wild flora and fauna and their natural habitats which require cooperation between states.
The following NATURA 2000 protected areas are located within the Suski Poviat:
- PLH 12 001 - Babia Góra
- PLB 120011 - Babia Góra
- PLH 12 012 – Na Policy
- PLB 12 006 – the mountain range of Polica
- PLB 24 0023 - Beskid Mały
-
More information on protected areas >> see

A virtual walk around the Suski Poviat > see